Faculty
Fabrizio Giansanti
Country: Italy
Affiliation: Eye Clinic, University of Florence, AOU Careggi
Image Bank
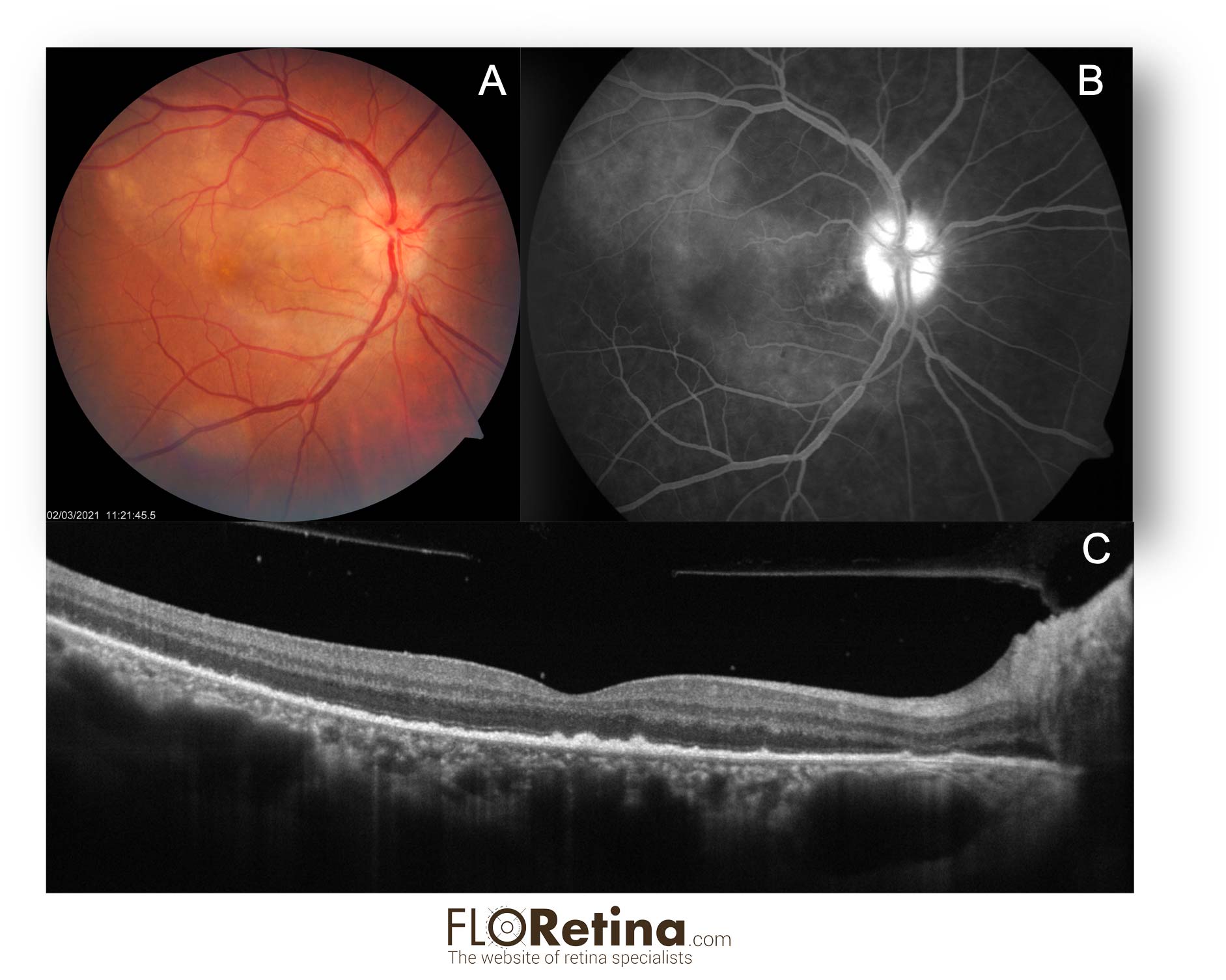
Acute Syphilitic Posterior Placoid Chorioretinopathy (ASPPC)
Daniela Bacherini Stefano Mercuri Fabrizio GiansantiA. Fundus photograph showing vast round placoid yellow zone in the posterior pole;
B. FA reveals hyperfluorescence of the optic disk with a zone of hyperfluorescence in the posterior pole (tissue staining).
C. Structural OCT shows disruption of the ellipsoid zone and hyperreflective, nodular thickening of the RPE. Hyperreflective dots representing inflammatory cells are visible in the vitreous and attached to the posterior hyaloid.
DEVICE: Multimodal imaging: fundus photograph, FA, Structural OCT
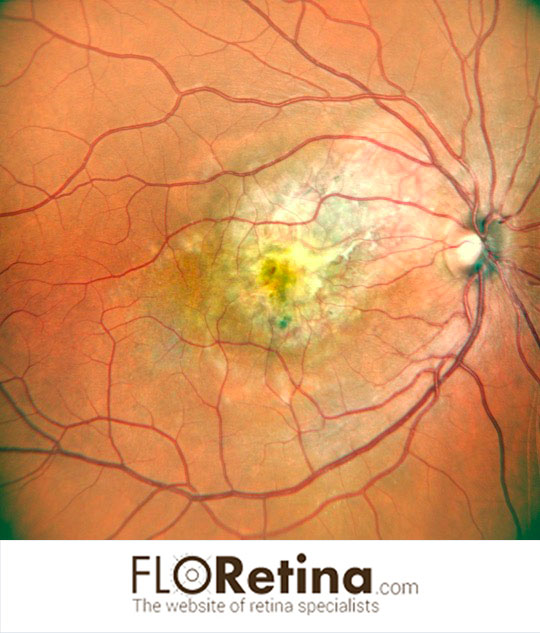
CHOROIDAL OSTEOMA complicated by choroidal neovascularization
Daniela Bacherini Stefano Mercuri Fabrizio GiansantiImaging device: Color fundus photography, angle 89°, Nidek
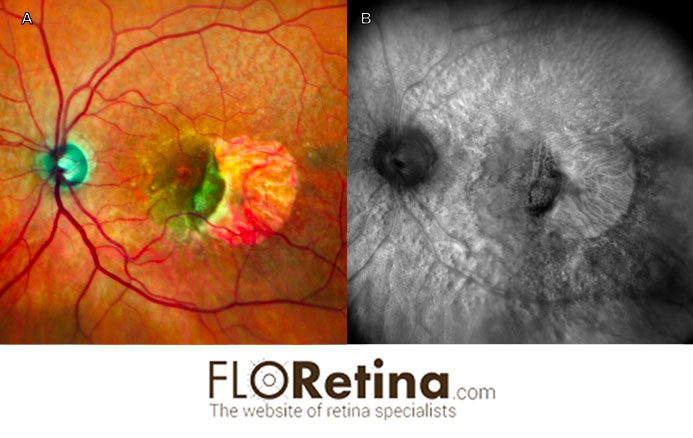
View imageRPE tear
Daniela Bacherini Fabrizio GiansantiImaging device: A. Color fundus photography, angle 89°, Nidek, B. retromode
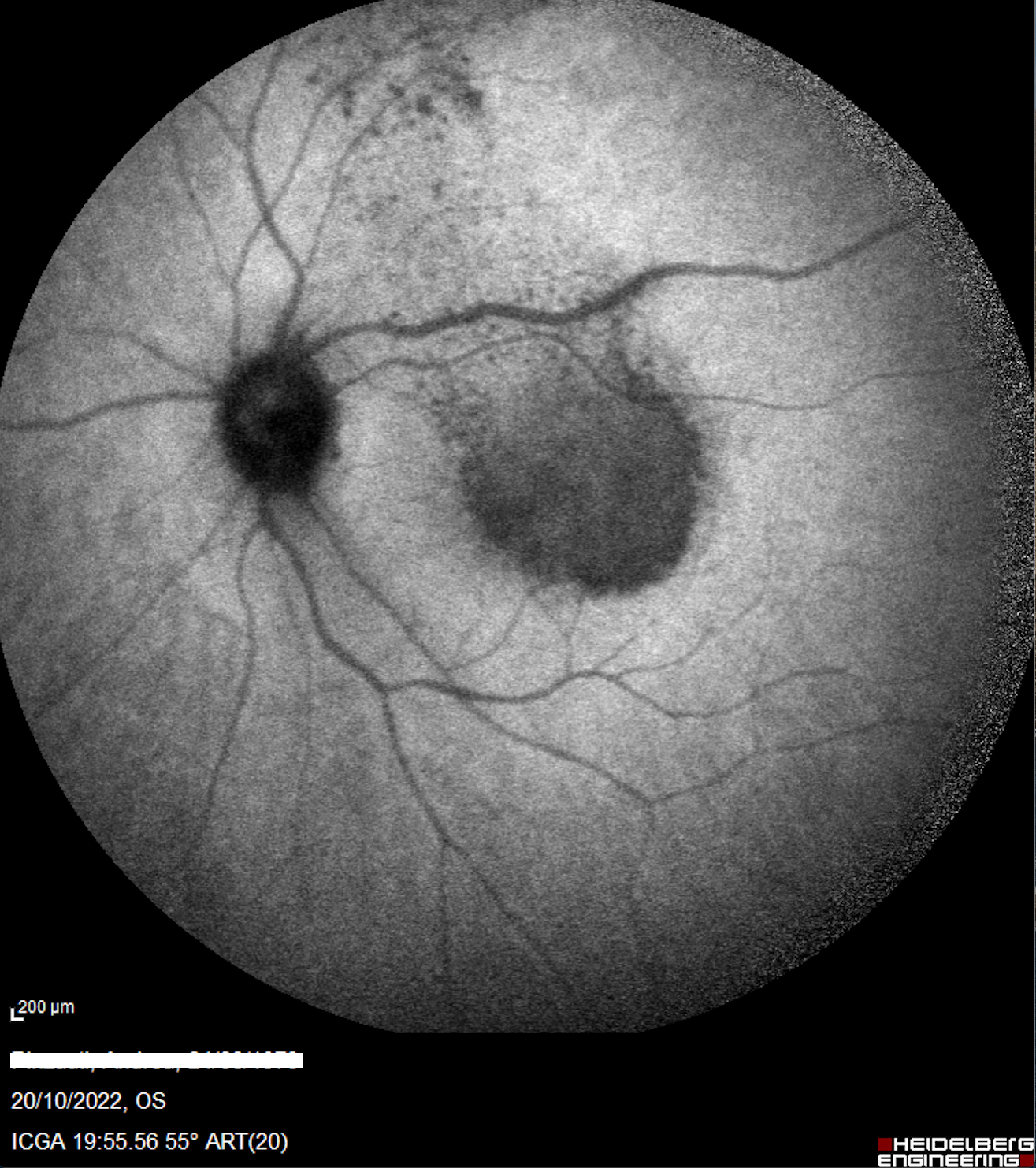
View imageSyphilitic posterior placoid chorioretinitis
Daniela Bacherini Giovanni Romualdi Fabrizio GiansantiA case of 49 y.o. man, caucasian, with no history of drugs and systemic disease, referred to our emergency room due to a sudden para central scotoma in his left eye. Our multimodal imaging allowed us to diagnose a syphilitic posterior placoid chorioretinitis, confirmed few days later with serological exams (qualitative TPHA +).
View imageClinical case
FAST DROP IN VISUAL ACUITY IN A 47 YEARS OLD MALE: SLOW DOWN WITH THE YELLOW!
Stefano Mercuri Daniela Bacherini Gianni Virgili Fabrizio Giansanti Acute syphilitic posterior placoid chorioretinitis (ASPPC) is a rare disease which may resemble many other retinal diseases.Multimodal imaging is important for diseases characterization, and new techniques may aid us in the understanding of their etiopathogenesis.
Accurate patient’s medical patient history is fundamental to spot the correct diagnosis as soon as possible with the purpose to avoid ocular complications and complications linked to syphilis progression.
© 2026 Copyright:
Floretina.com | P.I.
01477560138
Privacy Policy
|
Cookie Policy
|
Terms and Conditions